Lower Bounded Wildcard TypeS2C Home « Lower Bounded Wildcard Type
In the previous lesson we saw how we can use an Upper Bounded Wildcard Type when we have a scenario where we only want a method to work on a particular class or subtypes thereof. In this lesson we investigate the scenario where we only want a method to work on a particular class or supertypes thereof? In both of these situations we can use a bounded wildcard type to only allow certain types to use an identifier.
The table below lists the bounded wildcard types we can use with examples.
| Term | Examples | Notes | Lesson |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Bounded Wildcard Type | List<? extends Number> | Create a superclass boundary which all unknown types must be, or subtypes thereof. | Upper Bounded Wildcard Type |
| Lower Bounded Wildcard Type | List<? super Integer> | Create a subclass boundary which all unknown types must be, or supertypes thereof. | This lesson |
Lets look at a code example of using the lower bounded wildcard type.
Ok, lets start by creating and building some simple classes:
package com.server2client;
public class A {
{
System.out.println("A Object initializer");
}
}
package com.server2client;
public class B extends A {
{
System.out.println("B Object initializer");
}
}
package com.server2client;
public class C extends B {
{
System.out.println("C Object initializer");
}
}
package com.server2client;
public class D { // Nothing to do with other classes
{
System.out.println("D Object initializer");
}
}
Build the classes in the usual way.
Now we need to write a simple generic class that will take any type and have a method within in that will eventually only work on the B class and superclasses of it; first we will let
the method work with any type:
package com.server2client;
/*
Simple generic class that accepts any object
*/
public class LowerBoundedWildcardType<T> {
// Generic object declaration
private final T genericObj;
// Pass reference to object of type T to our constructor
public LowerBoundedWildcardType(T genericObj) {
this.genericObj = genericObj;
}
// Output object type of LowerBoundedWildcardType to console
public void showObjectType(LowerBoundedWildcardType<T> obj) {
System.out.println("Object type of LowerBoundedWildcardType is " + genericObj.getClass().getName());
}
}
Building the LowerBoundedWildcardType class produces the following output:
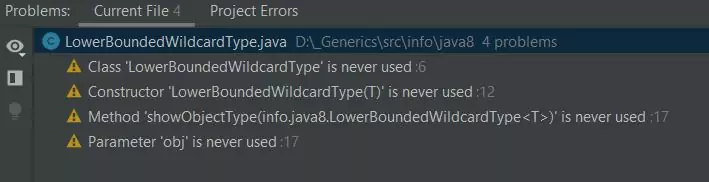
LowerBoundedWildcardType class.Now we need to write a test class to show how we can pass various objects to our BoundedWildcardType class:
package com.server2client;
/*
Test our LowerBoundedWildcardType class that accepts any object
*/
public class TestLowerBoundedWildcardType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create some objects
A a = new A();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
// Test the LowerBoundedWildcardType using A, B, C and D objects
LowerBoundedWildcardType<A> genAObj = new LowerBoundedWildcardType<>(a);
genAObj.showObjectType(genAObj);
LowerBoundedWildcardType<B> genBObj = new LowerBoundedWildcardType<>(b);
genBObj.showObjectType(genBObj);
LowerBoundedWildcardType<C> genCObj = new LowerBoundedWildcardType<>(c);
genCObj.showObjectType(genCObj);
LowerBoundedWildcardType<D> genDObj = new LowerBoundedWildcardType<>(d);
genDObj.showObjectType(genDObj);
}
}
Running the TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class produces the following output:
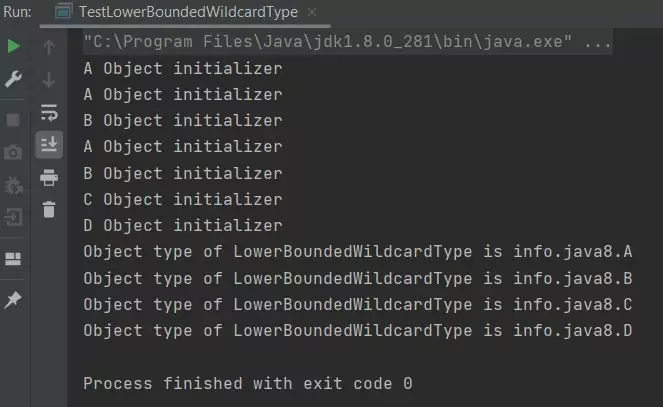
TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class.Well nothing new here, all the classes run as expected. Now we want to change the LowerBoundedWildcardType class so that only objects of type B or superclasses thereof can use the
showObjectType(LowerBoundedWildcardType<T> obj) method and for this we need a lower bounded wildcard type.
Change the signature to showObjectType(LowerBoundedWildcardType<? super B> obj) as shown below and rebuild the LowerBoundedWildcardType class.
package com.server2client;
/*
Simple generic class that accepts any object
*/
public class LowerBoundedWildcardType<T> {
// Generic object declaration
private final T genericObj;
// Pass reference to object of type T to our constructor
public LowerBoundedWildcardType(T genericObj) {
this.genericObj = genericObj;
}
// Output object type of LowerBoundedWildcardType to console
public void showObjectType(LowerBoundedWildcardType<? super B> obj) { // Changed to lower bounded wild card type
System.out.println("Object type of LowerBoundedWildcardType is " + genericObj.getClass().getName());
}
}
Rebuilding the TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments produces the following output:
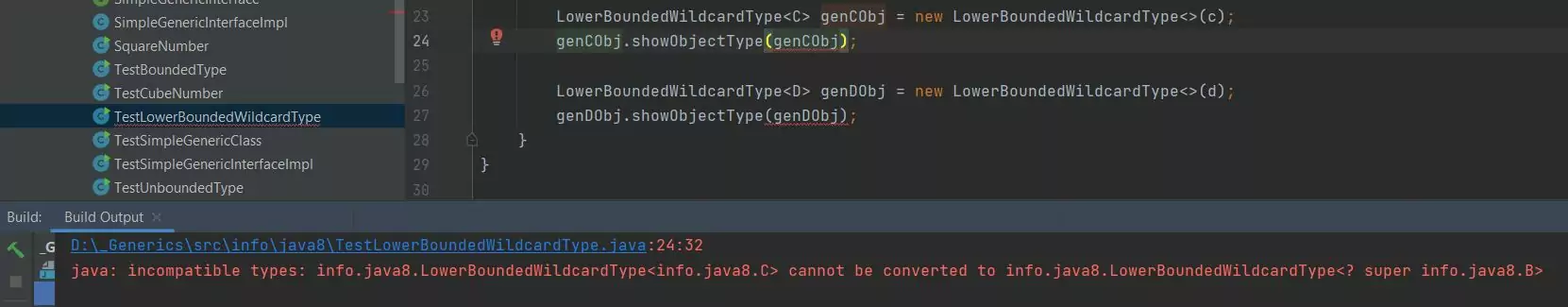
TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments.As you can see from the screenshot above the compiler won't allow us to call the showObjectType(LowerBoundedWildcardType<? super B> obj) method with an object of class C or D because
the method now has a lower bounded wildcard type that only allows the B class and its superclasses.
Remove the creation and call for the genCObj and genDObj in the TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class for the C and D types as shown below and rebuild the TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class.
package com.server2client;
/*
Test our LowerBoundedWildcardType class that accepts any object
*/
public class TestLowerBoundedWildcardType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create some objects
A a = new A();
B b = new B();
// Test the LowerBoundedWildcardType using A, and B objects
LowerBoundedWildcardType<A> genAObj = new LowerBoundedWildcardType<>(a);
genAObj.showObjectType(genAObj);
LowerBoundedWildcardType<B> genBObj = new LowerBoundedWildcardType<>(b);
genBObj.showObjectType(genBObj);
}
}
Rerunning the TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments produces the following output:
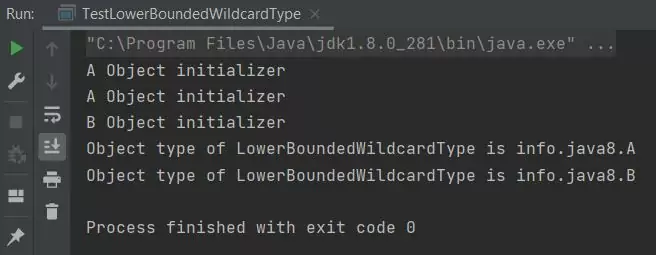
TestLowerBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments.Related Quiz
Generics Quiz 8 - Lower Bounded Wildcard Type Quiz
Lesson 8 Complete
In this lesson we looked at the generic lower bounded wild card type and how to use it.
What's Next?
In the next lesson we look at generic methods.