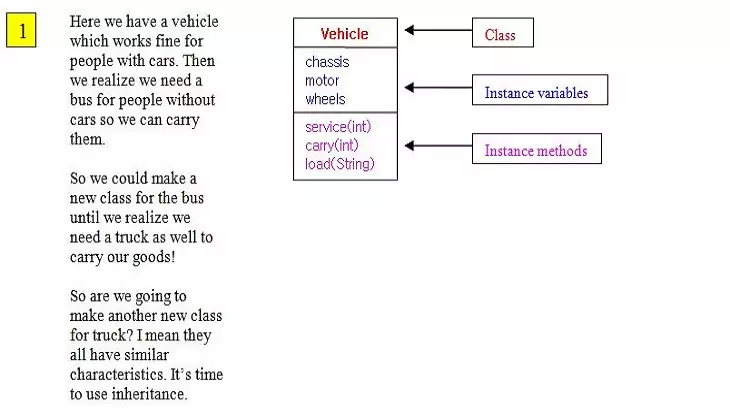
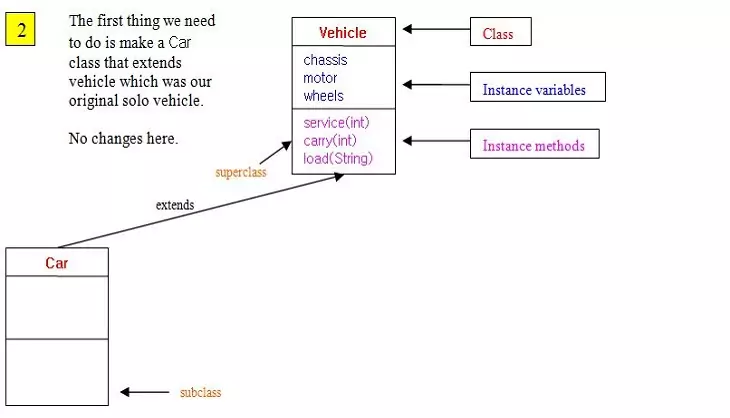
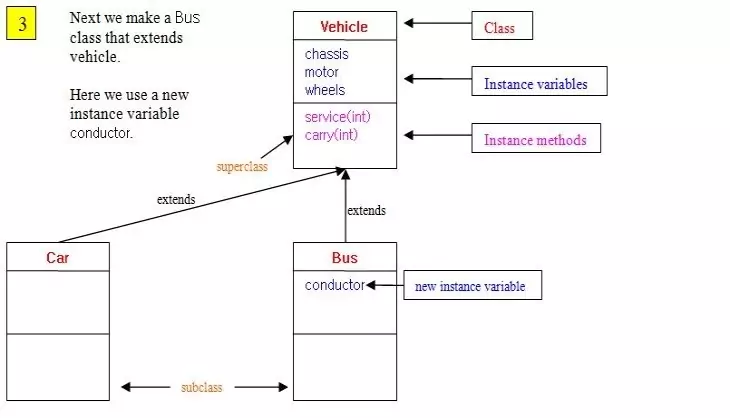
Inheritance - Using extendsS2C Home « Inheritance - Using extends
In the Inheritance - Basics lesson we took a first look at the concept of inheritance and how in Java terminology, the general class that holds the group of common characteristics is known as the superclass and the specialised subset of this is known as the subclass. We achieve this hierarchial connection in Java using the extends keyword, wherein the subclass extends the superclass.
In this lesson we use the extends keyword to create a couple of subclasses for the Vehicle superclass.
Following is a slideshow to digest the information we have written so far about inheritance:
Using the extends keyword
As metioned earlier in the lesson we create an inheritance tree in Java using the extends keyword, wherein the subclass extends the superclass. By extending like this we create an inheritance
hierarchy where we can use the more abstract superclass members, as well as more specific subclass member overrides where required. We will look at overriding methods in the next lesson.
Ok, time to code up the first two classes of the hierarchy shown in the slide show above, starting with the Car class.
Our Car subclass Top
Here we code and test the Car subclass where we use the extends keyword for the first time to subclass the Vehicle class. The Car class is very simple as
it just uses all the same members as its superclass, the Vehicle class.
package com.server2client;
/*
A Car Class
*/
public class Car extends Vehicle {
}
Save and compile our Car subclass in directory c:\_OOConcepts in the usual way.
When using the extends keyword to extend a class an important point to remember is you can only extend one class in Java. You can't say for instance:
package com.server2client;
public class Car extends Vehicle, Motorized {
}
As you will get a compiler error. We will go into more detail of this later in the section, for now lets test the new Car subclass to make sure it works:
package com.server2client;
/*
Test Class for Car
*/
public class TestCar {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Car estate = new Car();
estate.setChassis("2-axle chassis");
estate.setMotor("6 valve");
estate.setWheels(4);
System.out.println("Our car has a " + estate.getChassis() + ", " + estate.getMotor()
+ " motor and has " + estate.getWheels() + " wheels.");
estate.service(12);
estate.carry(6);
estate.load("shopping.");
}
}
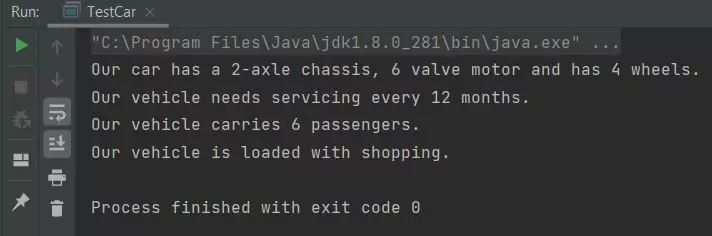
TestCar class.The above screenshot shows the output of running our TestCar class.
The above screenshot shows the output of testing our Car subclass. The class works as intended and uses all its inherited members of the Vehicle superclass to output some messages.
Time to code up our second subclass, the Bus class:
Our Bus subclass Top
Here we code and test the Bus subclass where we use the extends keyword again to subclass the Vehicle class. With the Bus class we need to add a new
instance variable conductor to the class. The superclass Vehicle has the rest of the stuff we need.
package com.server2client;
/*
A Bus Class
*/
public class Bus extends Vehicle {
private boolean conductor;
/*
Public getters and Setters
*/
public boolean getConductor() {
return conductor;
}
public void setConductor(boolean conductor) {
this.conductor = conductor;
}
}
Save and compile our Bus subclass in directory c:\_OOConcepts in the usual way.
Lets test the new Bus subclass to make sure it works:
package com.server2client;
/*
Test Class for Bus
*/
public class TestBus {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Bus a1 = new Bus();
a1.setChassis("4-axle chassis");
a1.setMotor("12 stroke");
a1.setWheels(8);
a1.setConductor(false);
System.out.println("Our bus has a " + a1.getChassis() + ", " + a1.getMotor()
+ " motor and has " + a1.getWheels() + " wheels.");
if (a1.getConductor()) {
System.out.println("This bus has a driver and a conductor.");
} else {
System.out.println("This bus has a driver only.");
}
a1.service(3);
a1.carry(60);
a1.load("people.");
}
}
TestBus class.The above screenshot shows the output of testing our Bus subclass. The class works as intended and uses all its inherited members of the Vehicle superclass as well as the new
instance varible conductor to output some messages.
Related Quiz
OO Concepts Quiz 4 - Inheritance - Using extends
Lesson 4 Complete
In this lesson we continued our investigation of Inheritance by using the extends keyword to subclass our classes.
What's Next?
We delve further into inheritance by looking at overriding methods.