Primitives - Numeric data typesS2C Home « Primitives - Numeric data types
In this lesson we take a much closer look at the numeric primitive variable data types available in Java.
The following table gives information on the numeric primitive variable data types.
| Type | Meaning | Bit Width | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| signed numeric integers | |||
| byte | 8-bit integer | 8 | -128 to 127 |
| short | Short integer | 16 | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| int | Integer | 32 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| long | Long integer | 64 | -9,233,372,036,854,775,808 to |
| signed floating point | |||
| float | Single-precision float | 32 | ≈ ±3.40282347E+38F (6-7 significant decimal digits) |
| double | Double-precision float | 64 | ≈ ±1.79769313486231570E+308 (15 significant decimal digits) |
Signed Numeric Integer Types Top
Java has 4 numeric integer types byte, short, int and long.
| Type | Meaning | Bit Width | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| byte | 8-bit integer | 8 | -128 to 127 |
| short | Short integer | 16 | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| int | Integer | 32 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| long | Long integer | 64 | -9,233,372,036,854,775,808 to |
As you can see you have a choice of four different sized containers to store your integer values in. So using the correct integer type for your needs saves some bytes. You can assign one primitive integer type to another as long as the assignment is to a larger container. If you try to assign a larger integer type to a smaller the compiler throws an error and won't allow it. You can create the following class in your IDE and cut and paste the code into it.
package com.server2client;
/*
Initialising and using numeric integer primitives
*/
public class IntTypes {
public static void main (String[] args) {
byte aByte = 128;
System.out.println("aByte = " + aByte);
short aShort = 642;
System.out.println("aShort = " + aShort);
int anInt = 12;
System.out.println("anInt = " + anInt);
long aLong = 3672543567;
System.out.println("aLong = " + aLong);
aShort = anInt;
System.out.println("aShort = " + aShort);
aLong = aByte;
System.out.println("aLong = " + aLong);
}
}
Running the IntTypes class produces the following output:
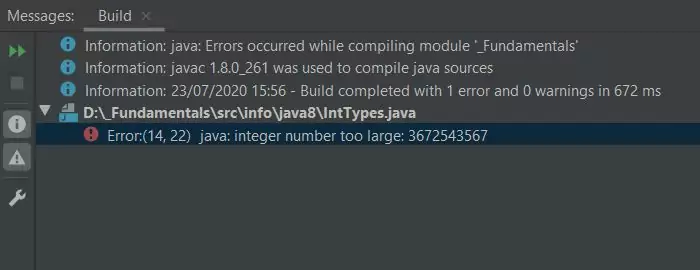
IntTypes class - Attempt 1.Ok the compile has failed with an error as shown in the screenshot and we get our first look at a compiler error. The reason for this is that when we pass a
literal value to a long we need to append l or L to it or the compiler inteprets it as an integer. Because an integer has a range of
-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 the number is out of range even though we passed it to a long
primitive type. We looked at literals in the Java Variables - Java Literals lesson; lets correct our code and append an L to it. I suggest always using an
uppercase L when specifying a long literal as a lowercase l looks a lot like the number 1. So edit your code and add the
L to the end of the number so you now have 3672543567L.
Rerunning the IntTypes class produces the following output:
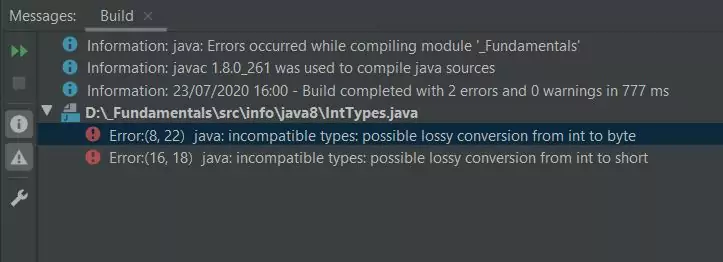
IntTypes class - Attempt 2.Ok the compile has failed again with two more errors as shown in the screenshot above. The first error is because we have given the variable aByte
a value of 128. The byte type range is -128 to 127 so this is out of range. Change this to 127 to fix
this error. The second error happens because we are trying to put an int into a short.
Even though the value contained in the variable anInt of 12 easily fits into the range of a short -32,768 to 32,767
the compiler just sees an int trying to be squeezed into a short and won't allow it. So let's change this to aByte from
anInt as follows aShort = aByte;.
Rerunning the IntTypes class produces the following output:
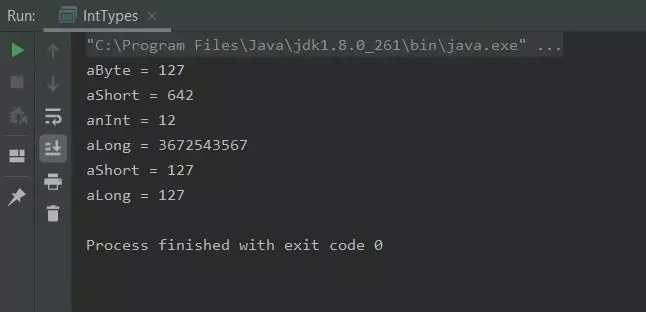
IntTypes class - Attempt 3.Well we got there in the end and as you can see the Java compiler isn't always as intuitive as we would like. Sometimes the compiler points to the wrong line or points to a place above or below the error. With practice you get used to compiler errors and you will get plenty of that as you write your Java code :).
Numeric Integer Test
Try this to test your knowledge of numeric integer types. Read down the list and check those you think will compile. Treat the list as a sequence of statements.
Signed Floating-Point Types Top
Java has 2 floating-point types float and double.
| Type | Meaning | Bit Width | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| float | Single-precision float | 32 | ≈ ±3.40282347E+38F (6-7 significant decimal digits) |
| double | Double-precision float | 64 | ≈ ±1.79769313486231570E+308 (15 significant decimal digits) |
Floating-point types represent non-integer numbers that have a fractional component and come in two flavours as described in the table above. Floating-point
types default to the double type unless we append an f or F when we initialize them. When this happens the compiler fails
as it thinks we passed a double to a float primitive.
You can create the following class in your IDE and cut and paste the code into it.
package com.server2client;
/*
Initialising and using numeric floating-point primitives
*/
public class FloatTypes {
public static void main (String[] args) {
float aFloat = 12.34F;
System.out.println("aFloat = " + aFloat);
double aDouble = 642.2761;
System.out.println("aDouble = " + aDouble);
// Dynamically initialized runtime by other variables
double bDouble = aFloat * aDouble;
System.out.println("bDouble = " + bDouble);
}
}
Below is the screenshot of running this code. Notice that the floating point doesn't display the F its just our way of telling the compiler this
is a float primitive. The other interesting point is variable bDouble which is dynamically initialized at runtime from the other two variables
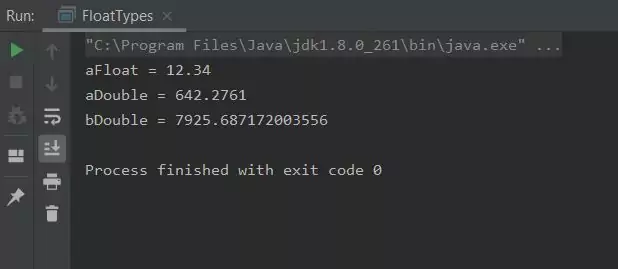
FloatTypes class.Related Quiz
Fundamentals Quiz 4 - Primitives - Numeric data types Quiz
Lesson 5 Complete
In this lesson we looked at the numeric primitive variable data types available in Java.
What's Next?
In the next lesson we look at method scope and what scope and its definition mean.