Model Part 1 - ExceptionsS2C Home « Model Part 1 - Exceptions
In this section of the case study we look at the model part of the MVC paradigm. In these four lessons we code as much of the model as we can from the information provided within the Project Proposal. The stakeholder Stocking Goods Limited have supplied us with a Stock interface that must be implemented and from this we can also derive some exception classes. In our first lesson of the section we code up the Stock interface exceptions for our model code and compile them.
Stock Interface Exceptions Top
The exception classes we need to code to
honour the contract of the Stock interface are DuplicateKeyException, RecordNotFoundException and SecurityException. So to get a clean compile on the the Stock Interface we will need to code up these exceptions first. All the exception classes are similar and allow us to throw an exception alone, with a message or chained and all of these classes extend the RuntimeException class. All the exception classes can be thrown remotely and so are serialized and use a version number so that serialisation can occur without worrying about the underlying class changing between serialization and deserialization.
We also decided in the Proposal Conclusions that a situation might arise where a user tries to stock goods that have already been stocked by
another user and if this happens we will need to throw a StockingException and so we will also create and compile this class.
Compiling The DuplicateKeyException Class Top
The following DuplicateKeyException class will be be thrown when we try to create a record that already exists.
Cut and paste the following code into your text editor and save it in the c:\_Case_Study\src\model directory.
package model;
/**
* Holds any duplicate key exceptions that may occur in the StockImpl class.
*
* @author Charlie
* @version 1.0
* @see StockImpl
*
*/
public class DuplicateKeyException extends RuntimeException {
/**
* A version number for the DuplicateKeyException class so that serialisation
* can occur without worrying about the underlying class changing
* between serialisation and deserialisation.
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2498052502L;
/**
* Create a default DuplicateKeyException instance.
*
*/
public DuplicateKeyException() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a DuplicateKeyException instance that accepts a String.
*
* @param e The string description of the exception.
*/
public DuplicateKeyException(String e) {
super(e);
}
/**
* Create a DuplicateKeyException instance and chain an exception.
*
* @param e The exception to wrap
*/
public DuplicateKeyException(Throwable e) {
super(e);
}
}
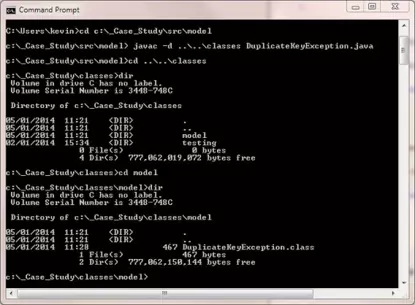
Compiling Our Source File With the -d Option
Open your command line editor:
Change to directory cd c:\_Case_Study\src\model
Compile DuplicateKeyException.java using the java compiler with the -d option
javac -d ..\..\classes DuplicateKeyException.java
Because we have used a package (package model;) at the top of the code the compiler has created this directory within the classes directory. When we look in the model
directory we can see the compiled DuplicateKeyException.class file.
Compiling The RecordNotFoundException Class Top
The following RecordNotFoundException class will be be thrown when we try to create a record that is not found which can occur when we try to read, update, delete or lock a record.
Cut and paste the following code into your text editor and save it in the c:\_Case_Study\src\model directory.
package model;
/**
* Holds any record not found exceptions that may occur in the StockImpl class.
*
* @author Charlie
* @version 1.0
* @see StockImpl
*
*/
public class RecordNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
/**
* A version number for the RecordNotFoundException class so that serialisation
* can occur without worrying about the underlying class changing
* between serialisation and deserialisation.
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2498052502L;
/**
* Create a default DuplicateKeyException instance.
*
*/
public RecordNotFoundException() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a RecordNotFoundException instance that accepts a String.
*
* @param e The string description of the exception.
*/
public RecordNotFoundException(String e) {
super(e);
}
/**
* Create a RecordNotFoundException instance and chain an exception.
*
* @param e The exception to wrap
*/
public RecordNotFoundException(Throwable e) {
super(e);
}
}
Compiling Our Source File With the -d Option
Open your command line editor:
Change to directory cd c:\_Case_Study\src\model
Compile RecordNotFoundException.java using the java compiler with the -d option
javac -d ..\..\classes RecordNotFoundException.java
Compiling The SecurityException Class Top
The following SecurityException class will be be thrown when we have a lock record mismatch which can occur when we try to update, delete or unlock a record.
Cut and paste the following code into your text editor and save it in the c:\_Case_Study\src\model directory.
package model;
/**
* Holds any security exceptions that may occur in the StockImpl class.
*
* @author Charlie
* @version 1.0
* @see StockImpl
*
*/
public class SecurityException extends RuntimeException {
/**
* A version number for the SecurityException class so that serialisation
* can occur without worrying about the underlying class changing
* between serialisation and deserialisation.
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2498052502L;
/**
* Create a default SecurityException instance.
*
*/
public SecurityException() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a SecurityException instance that accepts a String.
*
* @param e The string description of the exception.
*/
public SecurityException(String e) {
super(e);
}
/**
* Create a SecurityException instance and chain an exception.
*
* @param e The exception to wrap
*/
public SecurityException(Throwable e) {
super(e);
}
}
Compiling Our Source File With the -d Option
Open your command line editor:
Change to directory cd c:\_Case_Study\src\model
Compile SecurityException.java using the java compiler with the -d option
javac -d ..\..\classes SecurityException.java
Compiling The StockingException Class Top
The following StockingException class will be be thrown when a user tries to stock goods that have already been stocked by another user.
Cut and paste the following code into your text editor and save it in the c:\_Case_Study\src\model directory.
package model;
/**
* Holds any stocking exceptions that may occur in the StockImpl class.
*
* @author Charlie
* @version 1.0
* @see StockImpl
*
*/
public class StockingException extends Exception {
/**
* A version number for the StockingException class so that serialisation
* can occur without worrying about the underlying class changing
* between serialisation and deserialisation.
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2498052502L;
/**
* Create a default StockingException instance.
*
*/
public StockingException() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a StockingException instance that accepts a String.
*
* @param e The string description of the exception.
*/
public StockingException(String e) {
super(e);
}
/**
* Create a StockingException instance and chain an exception.
*
* @param e The exception to wrap
*/
public StockingException(Throwable e) {
super(e);
}
}
Compiling Our Source File With the -d Option
Open your command line editor:
Change to directory cd c:\_Case_Study\src\model
Compile StockingException.java using the java compiler with the -d option
javac -d ..\..\classes StockingException.java
Lesson 3 Complete
In this lesson we coded the exception classes for the Stock Interface.
Related Java Tutorials
Beginning Java - Primitive Variables
Beginning Java - Conditional Statements
Beginning Java - Loop Statements
Objects & Classes - Class Structure and Syntax
Objects & Classes - Reference Variables
Objects & Classes - Methods
Objects & Classes - Instance Variables & Scope
Objects & Classes - Constructors
Objects & Classes - Static Members
OO Concepts - Encapsulation - Getters & Setters
OO Concepts - Inheritance Concepts - Using the super keyword
OO Concepts - Interfaces
OO Concepts - The Object Superclass - Checking Object Equality
OO Concepts - The Object Superclass - The hashCode() Method
OO Concepts - The Object Superclass - The toString() Method
Exceptions - Handling Exceptions
Exceptions - Declaring Exceptions
Exceptions - Creating Our Own Exceptions
API Contents - Inheritance - Using the package keyword
API Contents - Inheritance - Using the import keyword
Concurrency - Synchronization - Synchronized Blocks
Swing - RMI - Serialization
What's Next?
In the next lesson we code and compile the Stock Interface.